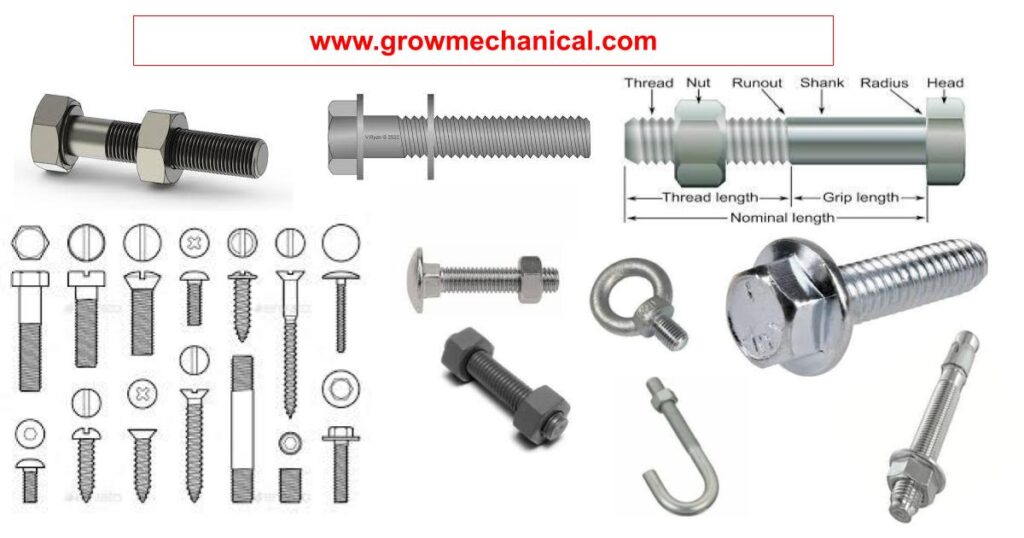
Pipe Flange
Pipe Flange is used to connect two different pipe, piping accessories like strainers, valves, or equipment nozzles like pumps, vessels, compressors, etc to each other for build a complete pipeline system. This is a circular plate with a set of small and big holes. The big hole is equally size to pipe OD, and the small holes are use for bolts and numbers of bolt holes on the pipe flange will be according to ASME B16.5 and ASME B.16.47.
There are two methods to connect pipe to pipe and pipe to equipment that is by the direct welding with pipe and equipment or by the help of flanges at both ends and then tighten with a nut bolt before tightening the flange and placing the gasket between both flanges. By connecting with the flange, three things are required that is flanges, nut bolts and gaskets. These are provide leak prof piping system.
There are some advantages and disadvantages of flanges connection.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| These are most expansive than weld joints, every time you need to replace the gasket when ever required to open | That is use where weld joints are not recommended due to welding restrictions, or not possible to install with weld joints. |
| always change of leakage between both flanges | Easy for maintenance and cleaning |
| More times are required to assemble | Required for equipment and pipes isolation |
| Less reliability than weld joints | Inspection can done easily even small portions of the pipeline system |
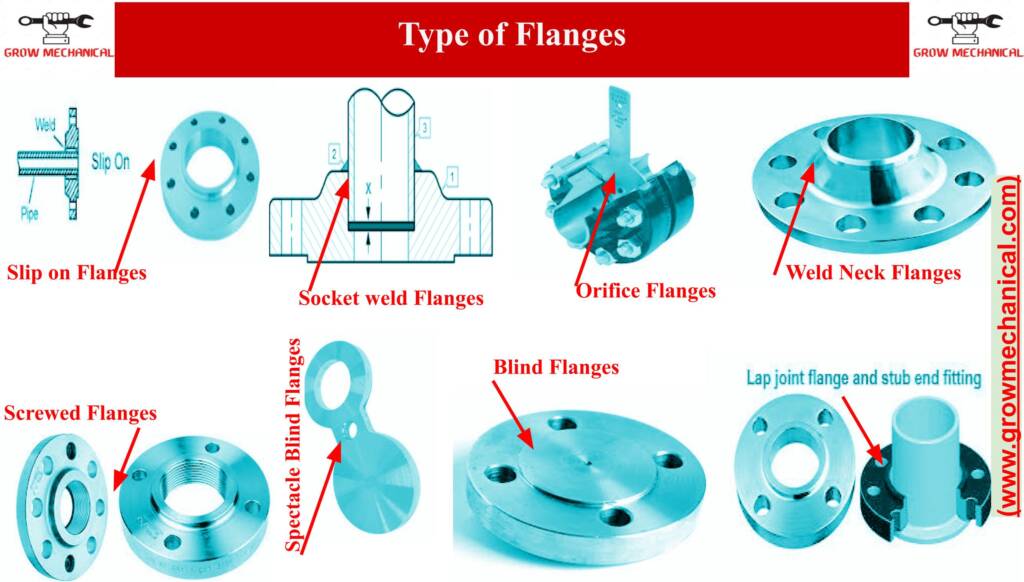
Type of Piping Flanges
There are many types of pipe flanges available and used accordingly to its application. Most commonly types are mentioned below.
| Slip On Flanges | Orifice Flange |
| Socket Weld Flanges | Screwed & Threaded Flanges |
| Weld neck Flanges | Square Flange |
| Lap Joint Flanges | Weldo Flange |
| Blind Flanges | Nippo Flange |
| Spectacle Blind Flanges | Plate Flange |
| Spade and Ring Spacer Flange |
Slip on Flanges
Slip on Flanges is a circular plate with inner hole slightly bigger to pipe OD. This is one of the most frequently used of flanges. As the name represents how that is connected to a pipe, for connect these types of flange slip over a pipe for fit-up so it is known as Slip On Flanges. A slip-on flange is also known as SO flange as sort name or fabrication language.
How to weld slip on flange with pipes
For welding of slip on flange with pipe, place slip on flange on the (OD) circumference of the pipe at one end, and maintain a required distance between both for weld and apply a welding to the inner diameter and outer diameter. That can be weld directly to equipment nozzle or pipe with fillet welding. Flange hole is slightly bigger than the pipe OD so easily slip over the pipe and weld to each other.
This is available with two types that is a raised and flat face and both are used depending on its applications.
The raised face Slip-On Flanges are called SORF (Slip-On raised Flanges flanges) and are suitable for low and high pressure-temperature applications. These types of flanges have some advantages over other types of flanges that are low cost, used for ease of assembly.
Design and Dimension standard for slip on flanges
ASME B16.5 the up to 24 inches diameter pipe flange, ASME B16.47 Series A & B used for above the 24 inches diameter pipe flange.
Dimension standard BS10 MS, CS, SS 304/316/317 and other material pipe flange.
Socket weld Flange
Socket weld flanges are only connected by one fillet weld joint on the outside flange. This is similar to slip on flange and tensile strength is also equivalent to slip on flanges, but their fatigue strength is 50 percent higher than double-welded Slip On flanges. Socket-weld pipe flanges are typically used on smaller diameter pipe up to 2 inch and high pressure pipes connection.
How to weld socket weld flange with pipes
These flanges are attached by inserting the pipe into the socket end flange and applying fillet weld around the top. Before starting welding, a gap (X) must be maintained between socket weld flange socket end and pipe end. The objective of a Socket Weld’s bottom clearance is generally to minimize the residual pressure at the weld root that could occur during weld metal solidification.
This allows for a smooth bore and better flow of the fluid or gas inside of the pipe. Fits over recessed portion. Weld on the back.Good for small diameter 2” and below.
Design and Dimension standard for slip on flanges
- ASME B16.5 the up to 24 inches diameter pipe flange, ASME B16.47 Series A & B used for above the 24 inches diameter pipe flange.
Dimension standard BS10 MS, CS, SS 304/316/317 and other material pipe flange.
Weld Neck Flanges are commonly used for high pressure applications up to 50000 psi also called as second name tapered hub flange or high-hub flange. Weld neck flange has a neck that reduces connecting pipe stress, thereby reducing the pressure gathered in the bottom of the flange. It can withstand high or low temperature-pressure application. Welding Neck Flanges can be easily identifiable at the long-tapered end, which diameter reduces through the wall thickness toward its neck fitting. The long-tapered hub provides strength for use in multiple applications likes high pressure, sub-zero or high temperatures.
This type of flange is designed to butt weld directly with pipe for a superior and natural form connection. As shown in the picture. Mostly used flanges for above 2-inch pipe size.
Advantages of weld neck Flange
- Used in severe high pressure & temperature services.
- Can withstand repeated bending.
Design and Dimension standard for weld neck flanges
Weld neck flange dimensions are covered in ASME B16.5 – which covers Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings for size NPS ½” to 24”. For above NPS 26” to 60” it should be as per ASME B16.47.
Lap joint flanges
A lap-joint flange is assembled as a two-component, a stub end that is used with a lap-joint ring flange. During setup, the ring flange place over it. This type of flange connection is particularly useful for large or hard-to-adjust flanges. Lap joint flanges are used when the pipe and stub end pipe are made of more costly material so with that stub end carbon steel or other flange’s material can be used. Because flanges do not come into directly contact with the inside fluid or substance within the pipe.
How to weld lap joint flange with pipes
The stub ends will be butt-welded to the connecting pipe and the flanges will remain (free to rotate) loose, and the flange ring can be rotated to align and match the bolt circle with the other mating flange. .
Lap joint flanges are similar to the Slip On flange, except that it is not directly weld with pipe
Advantages and disadvantages of Lap joint flange
- It is best for low pressure and used for non-critical applications.
- The fatigue life of the assembly is only one-tenth that of the Weld Neck flanges.
- Less expansive than other types of flange
Blind Flanges
Blind Flange is a blank flange without hole that is used to prevent or isolate the fluid from coming outside of the pipeline (that is installed at the end of the pipe section, equipment nozzle), valves and pressure vessel openings. The measure function of these flanges is to obstruct a segment of the pipe, nozzle of the vessel that is not in use or any test required, like hydro test, leak test, or maybe performed any maintenance or shutdown activity. These types of flanges are able to sustain lower, medium and higher pressure temperature systems. There is no pipes connected at the other end of the flange.
Types of blinds flanges
There are two types of blinds flanges that are flat face (FF) and Raised face (RF) blind flange.
A flat face flange is completely smooth on the front face across the surface. The raised face flange has a slightly elevated middle area (Serrated area) that creates two levels on the surface of the flange. The blind flange is fitted with other type flanges by bolting method.
Spectacle Blind Flanges
Spectacle blinds flange are installed for permanent purposes to separate the one pipeline to the other pipeline of single systems or to connect with pipeline to the other pipeline or pipeline to the equipment. That is always installed between the two different pipe flange along with two gaskets both side of the spectacle blind flange. A Spectacle Blind is used like a blind flange but there are two discs connected in which one is blank dick and the other one is with a hole equal to the size of pipe ID and with certain thickness. The two discs are joint to each other by the help of a thick strip steel plate. One of the discs is a solid blank plate like as blind flange but there are no bolts hole within it, and the other is a ring, whose inside diameter is equal to that of a pipe flange ID. Maybe changes in some special requirement.That is not most preferred use with a big bore pipe line like more than 12”.
Spade and Ring Spacer Flange
Spades and Ring Spacers are used for the same purposes as Spectacle Blinds, but both are not connected to each other. These are available in two separate part as shown in figure. Spades and Spacers applies in systems where maintenance possibility is very less or occasionally.that is used with large pipe sizes. Depending on the flange size and pressure class, spades have less weight than a spectacle blind flange so that is the reason for mostly not preferred choice of spectacle blind. High maintenance of the pipe system can be a major reason to temporarily replace the Ring Spacer with a spade. Note- for identifying visually differences between Spades and Ring Spacers, a hole is provided on the tell of the spade, and two small holes on the tell of the ring spacer as shown in the figure.
The sealing surfaces of a Spectacle Blind, Spade or Ring Spacer are usually in accordance with the Face Finish from the design standard ASME B16.5. The diameter is always slightly larger than the raised face of a flange. ASME B16.48 covers pressure-temperature ratings, materials, dimensions, dimensional tolerances, marking, and testing for operating lines. Spectacle Blinds, Spades and Ring Spacers should be made from a plate or forging, but specification should be followed as per ASME B31.3.
Formula to calculate the thickness of a spacer
As a rule of thumb calculate the thickness of spacer in MM. Pressure (barg) multiply by diameter (inches) divided by 10 Pressure is the highest pressure that the system can achieve. Diameter the size of the spacer in inches, Example 8 x 12 / 10 =thickness of spacer = 9.6 m.
Note. ASME B16.5 also covers spectacle blind thickness.
Orifice Flanges
Orifice Flanges are a flat thick plate like spade flange but it is thicker than that & a little drill hole in the center or off center of it. This is used with orifice meters for measuring the flow rate of services fluid (liquids, gases). Pairs of pressure taps, on both sides directly opposite from each other, are made onto the orifice flange by machining. Orifice Flange Unions are designed & manufactured to AGA, ASME, & ISA recommendations. There are some important types of Orifice Flanges available: Raised Face weld neck orifice flanges, Raised Face slip-on orifice flange, Ring-Type joint weld neck orifice flanges, Corner tap orifice flanges, that is used according to end user requirements. The complete orifice flange assembly consists of a pair of flanges, orifice plate, bolts, nuts, 02 nos of gaskets, jacking screws and plugs. Orifice Flanges are used to measure the flow rate or pressure drop of liquids or gases in a pipeline. Orifice plates are a primary flow element, detecting the flow of a fluid passing through the orifice plate by sensing the pressure drop across the plate. When a fluid flows through a restriction in a pipe, it creates a pressure difference between upstream and downstream of the restriction of the orifice flange. Orifice plates are instrument devices which are used for measure and control the fluid flow`.
Screwed & Threaded Flanges
Screwed Flange and Threaded Flange are interchangeably, and as its name, having a thread inside the flange bore which fits on the male pipe thread. These flanges are mostly used in utility services such as air and water. With small bore pipe and high pressure. Screwed flanges with a hub have issued requirements ranging from 1/2′′ to 24′′. Pressure class: Class 150 to Class 2,500, PN 2.5 to PN 250 and Facing: RF / RTJ
The advantage of these flanges is that they connect without welding with less time.
Advantages Screwed Flanges
- No welding required.
- Used at low pressure, moderate temperature.
- Used for smaller size.
- Not suitable for services involving high thermal/bending stresses.
Design and Dimension standard for Screwed Flanges
ANSI B16.5, ANSI B16.47 Series A & B, MSS SP44, ASA, API-605, AWWA, Custom Drawings.
Square Flanges
Square flanges are most frequently used for stabilizing connections between pipe-to-pipe and pipe-to-equipment nozzles. Square flanges are constructs according to JIS B2291/JIS F7806 standards. They are most used in hydraulic services where a passage of fluids occurs and are made of two materials which are steel and stainless steel. A complete assembly of square flanges is as the o’ring, bolts, female flange (o ring side), and male flange (flat side).
Types of Squar flange
Square Flanges are divided into three types under this standard:
- SHAB – Used with hexagon hex bolts, larger flange body size,
- SSAB – Used with socket cap screw, smaller flange body size than SHAB,
- LSA – Oring side only, L shaped internal flow.
Weldo Flange / Nipo Flange
A Nipoflange is a combination of weldolet, Nippolet and Weld with Neck flange & widely used in the industry for 90° branch connection. On the run pipe side a weldolet flange is designed like a weldolet and on the other side, it has a flange connection. That means the branch connection on the run pipe side is a welding connection. In a Nipo Flange the branch connection on the run pipe side is a welding connection and on the other side, it has a flange connection.
Plate Flanges
Plate Flange is a type of flange, it has a gasket surface in the same plane without a raised face on the flange plane. It is also called simple flange or flat-faced flange. The applications of flat face flanges are used for low-pressure and temperature water piping. Flat face flanges are used when the equipment flanges are flat face and then bolt to each other with place a gasket within it.
Flanges – Dimensions & Design Standard
- Flanges – Dimensions & Design Standard
- Surfaces – Dimensions – Material ASME B16.48 The gasket seating surface finish and dimensions for raised face line blanks shall be in accordance with ASME B16.5.
- ASME B16.5 – Covers Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings for size NPS ½” to 24” for pressure Class 150 to 2500.
- ASME B16.47 covers up to NPS 26” to 60” diameter pipe for pressure Class 150 to 2500.
- ASTM A105 is the most take for carbon steel material grade that is used to manufacture forge piping components.
- ASTM A182 Standard Cover specification for forged alloy steel and SS materials, used for manufacturing pipe fitting for high-temperature and pressure service applications.
- ASTM A234/A234M : Standard cover specification of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for pipe fitting Moderate and High Temperature Service application.
- A350 is a general carbon steel materials grade that is supplied with a Normalised, Normalised and Tempered condition or a Quenched and Tempered condition.
- ASTM SA105N Standard covers only carbon steel flange for 18” to 42” Blind, Weld Neck, Lap Joint and slip on flange for classes 150 and 300.
- ASTM B16.11 Standard cover for the forged steel pipe fittings includes socket weld and threaded fittings type.
- ASME b16.9 Factory-Made Wrought Steel Butt-welding Fittings.
Flanges – Terminology
- Flat Face (FF): Flat face flanges have a flat surface, and the gasket fits with a full face between both flanges that contacts most of the flange surface area.
- Raised Face (RF): These flanges have a slightly raised section around the flange bore, between flange bore and bolt circle with serration for gasket fit up.
- Ring Joint Face (RTJ): Used in high-pressure and high-temperature processes, A groove is made on both flanges for metal gasket fit to maintain the seal.
- Male & Female (M&F): These flanges are used with matching pairs of grooves and raised sections to secure the gasket. in which one flange has a groove and another has a raised section.
- Outside diameter: Dimension of diagonally or opposite diameter of flange.
- Thickness: Thickness of the outer attaching rim of the flange.
- Bolt circle diameter: The distance between bolt hole to bolt holes and that measured from bolt hole centre to next bolt hole center.
- Pipe size: Bore size of pipe.
- Nominal bore: A measurement of the flange connected pipe bore.
How to select pipe flange
There are many parameters for selecting an appropriate pipe Flange some of the important technical details are given below.
- Size DN 50NB/100NB/200NB (2”/4”/8”) OR other
- Types of flange : Screwed, Slip On, SORF or other
- Dimensions standard ASME B16.47, MSS SP-43, ANSI B16.5 OR OTHER.
- Design standard ASTM A234 WPB, ASTM A105, ASTM F1545.
- Materials of construction (MOC), Mild steel (MS), Stainless steel (SS), Carbon steel,
- Class/Pressure rating/Schedule Class 150/300/600 or others
- End connection socket weld/Threaded/lap joint or other
- Weld required Socket weld or Butt weld.
- Corrosion resistance (Materials compatibility)
- Durability
Some More Interesting Articles You Can Also Read From Here.


