Sleeve bearings
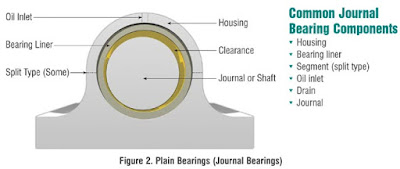
Sleeve bearings, also known as journal bearings, are a type of plain bearing that supports a rotating shaft using a cylindrical sleeve. The sleeve is typically made of a soft material such as bronze, brass, or a polymer like nylon or Teflon. The lubrication of the bearing is critical for its operation, and it is usually provided by an oil or grease film that forms between the shaft and the sleeve.
Sleeve bearings have several advantages, including their simplicity, low cost, and low noise operation. They are also capable of high shock absorption, making them suitable for applications with variable or high shock loads. Sleeve bearings are self-lubricating, which reduces friction and wear, and they can operate at low speeds and low loads. However, sleeve bearings are generally not suitable for high-speed or high-load applications, as they can generate excess heat and wear more quickly under these conditions.
Sleeve bearings are commonly used in a variety of industrial applications, such as motors, pumps, fans, and conveyors. They are also used in household appliances, such as washing machines, dryers, and refrigerators. The selection of the appropriate sleeve bearing depends on factors such as the load, speed, and temperature requirements of the application. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and inspection, is necessary to ensure the proper operation and longevity of sleeve bearings.
Types of plain bearing
There are several types of plain bearings, including:
- Sleeve bearings: Sleeve bearings, also known as journal bearings, are the most common type of plain bearing. They consist of a cylindrical sleeve that supports the rotating shaft and a layer of lubricant that separates the shaft and the sleeve.
- Flange bearings: Flange bearings have a flanged outer ring that is used to mount the bearing in place. They are often used in applications where the bearing needs to be secured in place.
- Thrust bearings: Thrust bearings are used to support axial loads, which are loads that are applied parallel to the shaft. They are often used in applications where the shaft needs to be supported in both axial and radial directions.
- Spherical bearings: Spherical bearings have a spherical inner ring that is used to compensate for misalignment between the shaft and the bearing. They are often used in applications where the shaft is subject to misalignment or bending.
- Hydrodynamic bearings: Hydrodynamic bearings use the motion of the lubricant to generate a fluid film between the shaft and the bearing. This fluid film reduces friction and wear, resulting in longer service life and higher efficiency.
- Magnetic bearings: Magnetic bearings use magnetic fields to levitate the shaft, eliminating the need for physical contact between the shaft and the bearing. This results in lower friction and wear, as well as lower maintenance requirements.
In summary, there are several types of plain bearings, including sleeve bearings, flange bearings, thrust bearings, spherical bearings, hydrodynamic bearings, and magnetic bearings. Each type of bearing has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the selection of the appropriate bearing depends on the specific application requirements.
The advantages and disadvantages Sleeve bearing
Advantage Sleeve bearing
- Sleeve bearings, also known as journal bearings, have several advantages:
- Simple Design: Sleeve bearings have a simple design and are easy to manufacture. They consist of a cylindrical sleeve that supports the rotating shaft, and a layer of lubricant that separates the shaft and the sleeve.
- Low Cost: Sleeve bearings are generally less expensive than other types of bearings, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
- Low Noise: Sleeve bearings produce less noise compared to other types of bearings, as they do not have rolling elements that can create noise.
- High Shock Absorption: Sleeve bearings have high shock absorption capabilities, which makes them suitable for applications with variable or high shock loads.
- Self-Lubrication: Sleeve bearings are capable of self-lubrication, as they rely on the lubricant film between the shaft and the sleeve to reduce friction and wear.
Disadvantaged of Sleeve bearing
- Sleeve bearings, also known as journal bearings, are a type of plain bearing that supports a rotating shaft using a cylindrical sleeve. Here are some disadvantages of sleeve bearings:
- Limited Load Capacity: Sleeve bearings have a limited load capacity compared to other types of bearings. They are not suitable for applications with very heavy loads.
- Friction: Sleeve bearings have higher friction compared to other types of bearings, which can result in higher energy consumption and lower efficiency.
- Wear: Sleeve bearings are subject to wear and tear over time. The bearing surfaces can become scratched or damaged, resulting in reduced performance and shorter service life.
- Lubrication: Sleeve bearings require regular lubrication to operate effectively. If they are not lubricated properly, they can experience excessive wear and tear.
- Misalignment: Sleeve bearings require proper alignment to function correctly. If the shaft is not aligned properly, the bearing can wear unevenly or fail prematurely.
In summary, sleeve bearings have a limited load capacity, higher friction, and require regular lubrication and proper alignment. They are not suitable for applications with heavy loads or high speeds, but they can be an effective and cost-efficient solution for low-speed and low-load applications.
Materials for plain bearing
Plain bearings are an essential component in machinery and equipment that allows two metal surfaces to slide over each other with minimal friction. The choice of metal used in plain bearing manufacturing depends on various factors, including load capacity, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions. Here are some of the commonly used metals in plain bearing manufacturing:
- Babbitt Metal: Babbitt metal is a soft, white metal that is commonly used as a lining material in plain bearings. It has excellent load-carrying capacity, low coefficient of friction, and good conformability. Babbitt metal is made of tin, copper, and antimony and is often used in high-speed and heavy-load applications.
- Bronze: Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin, with other elements added to improve its properties. It has good wear resistance, high strength, and is resistant to corrosion. Bronze is commonly used in plain bearings for medium to heavy loads, low to medium speeds, and moderate temperatures.
- Brass: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc that has good corrosion resistance, high ductility, and excellent machinability. It is commonly used in plain bearings for light to medium loads, low speeds, and moderate temperatures.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal that has good thermal conductivity and excellent machinability. It is commonly used in plain bearings for low to medium loads, low to medium speeds, and moderate temperatures.
- Steel: Steel is a strong and durable metal that has high resistance to wear and corrosion. It is commonly used in plain bearings for heavy loads, high speeds, and high temperatures.
In conclusion, the choice of metal used in plain bearing manufacturing depends on various factors such as load capacity, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions. Manufacturers may choose from a variety of metals such as Babbitt metal, bronze, brass, aluminum, and steel, based on the application requirements.
Working principle of plain bearing
Plain bearings are a type of bearing that supports the shaft by sliding against a stationary surface. The working principle of plain bearings is based on the principle of hydrodynamic lubrication. The lubrication layer is created between the sliding surfaces of the bearing and the shaft, which reduces the friction between them and prevents excessive wear.
The lubrication layer is created by a thin film of oil or other lubricants that are supplied to the bearing. The bearing is designed to have a slight clearance between the shaft and the bearing surface, which allows the lubricant to flow and form a thin film. The lubricant forms a wedge-shaped layer that supports the shaft and prevents it from touching the bearing surface. As the shaft rotates, the lubricant layer moves with it, creating a hydrodynamic pressure that supports the shaft and reduces friction.
Plain bearings are used in various applications, such as pumps, turbines, engines, and other machinery. They are preferred over rolling bearings in applications that require high loads, low speeds, and harsh environments. Plain bearings are also known for their durability, low maintenance, and long service life.
Comperision of plain bearing to ball and roller
Plain bearings, ball bearings, and roller bearings are all types of bearings that are used to support rotating shafts. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of bearing depends on the application requirements. Here is a comparison of plain bearings to ball and roller bearings:
- Load Capacity: Plain bearings have a higher load capacity compared to ball and roller bearings. They can support heavy loads and withstand shock and vibration.
- Friction: Plain bearings have higher friction compared to ball and roller bearings. This can result in higher energy consumption and lower efficiency.
- Speed: Ball and roller bearings can handle higher speeds compared to plain bearings. The rolling elements in ball and roller bearings reduce friction and allow for higher rotational speeds.
- Maintenance: Plain bearings require more maintenance compared to ball and roller bearings. They need to be lubricated regularly, and the bearing surfaces need to be periodically inspected and replaced.
- Durability: Plain bearings have a longer service life compared to ball and roller bearings. They are better suited for applications with high loads and harsh environments.
Comperision of plain bearing to tilting pad bearing
Plain bearings and tilting pad bearings are both types of bearings used to support rotating shafts. Here is a comparison between the two:
- Load Capacity: Tilting pad bearings have a higher load capacity compared to plain bearings. The pads in tilting pad bearings are designed to adjust to changes in load, allowing them to support very heavy loads.
- Friction: Tilting pad bearings have lower friction compared to plain bearings. The pads in tilting pad bearings are designed to rotate and reduce friction, which results in higher efficiency and less energy consumption.
- Speed: Tilting pad bearings can handle higher speeds compared to plain bearings. The pads in tilting pad bearings rotate freely, allowing for higher rotational speeds.
- Maintenance: Tilting pad bearings require more maintenance compared to plain bearings. The pads need to be lubricated regularly, and the bearing surfaces need to be periodically inspected and replaced.
- Durability: Tilting pad bearings have a longer service life compared to plain bearings. They are better suited for applications with high loads and high speeds.
In summary, tilting pad bearings have a higher load capacity, are more efficient, and can handle higher speeds compared to plain bearings. However, they require more maintenance compared to plain bearings. Plain bearings are more suitable for low-speed applications and require less maintenance, but have lower load capacity compared to tilting pad bearings. The choice of bearing depends on the specific requirements of the application.