FMECA (failure mode effects and criticality analysis)
The (FMECA) failure mode effects and critical analysis method is used to identify and prioritize failures that could occur in the processing system or particular equipment. It is a part of FMEA. With the help of failure mode effects and criticality analysis to identify what types of maintenance could be done on different equipment based on criticality and risk.in the all process, the FMECA sheet is very useful for analysis. And Fmeca sheet is prepared by the plant engineers, managers, and other support team members for each system.
How many types of failure mode effect and criticality analysis?
- Design FMECA
- Process FMECA
- Mechanical FMECA
Design FMECA
FMECA is also used for designing of equipment. Design FMECA is to identify and eliminate failures that could occur during the operation of equipment and plants.
Process FMECA
The process FMECA focuses on the problem of the equipment and failure could occur when the operation during the operation of equipment.
Mechanical FMECA
Failure mode effects and critical analysis is totally based on the calculation of the RPN number, and by the help of the RPN number identifies what type of maintenance will be done on which equipment because it is the total quantity number and rank. The equipment rank is also decided. With the help of the RPN number, RPN the number is not fixed. It changes equipment to equipment and plant to plant on the base of S, O, and D. The value of S, O, and D is varied from 1 to 10. The formula used for calculation of RPN number is
RPN = O X S X D, RPN numbers could vary from 1 to 1000. The RPN number has not any units.
FMECA, RPN number calculation sheet
|
Compressor
|
O
|
S
|
D
|
RPN
|
|
Dry gas seal
|
8
|
8
|
7
|
RPN = o x s x d
448,216,6
|
|
Bearing
|
6
|
6
|
6
|
|
|
Shaft
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
|
Gearbox
|
12,180,4
|
|||
|
Gears
|
2
|
2
|
3
|
|
|
Bearing
|
5
|
6
|
6
|
|
|
Shaft
|
1
|
2
|
2
|
|
|
Motors
|
90,6,24
|
|||
|
Bearing
|
3
|
5
|
6
|
|
|
Rotor
|
1
|
3
|
2
|
|
|
Bearing isolator
|
2
|
2
|
6
|
|
How to identify the FMECA?
Analysis of FMECA is totally based on three parameters listed below
- The severity of equipment failures.
- The occurrence of equipment failures.
- Detectability of equipment failure.
How can we apply the failure mode critical analysis for the maintenance of the equipment?
- Provider maintenance planning
- Maintain history record and documentation of equipment
- When the last failure occurs and identifies the frequency of failure and severity the same.
- Provide quantitatively, reliability, and availability of equipment.
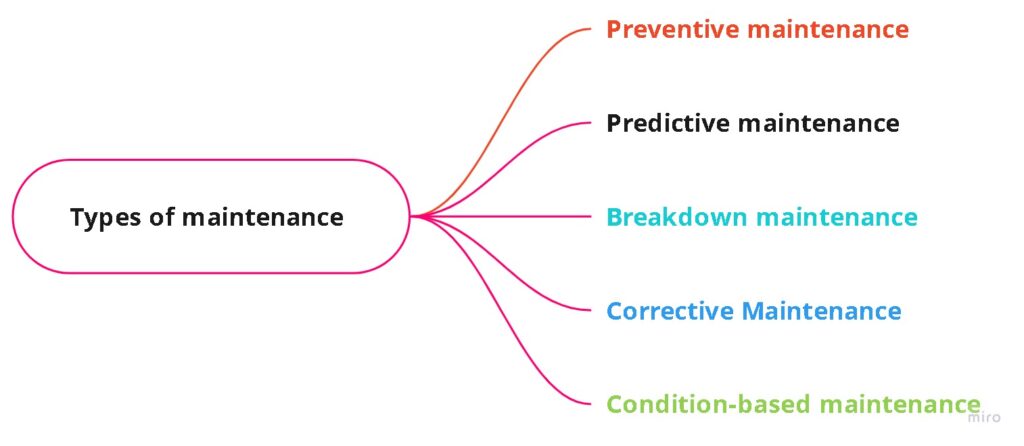
Now we discuss FMECA for maintenance planning and selection.
- Preventive maintenance (Periodic)
- Predictive maintenance (condition-based maintenance)
- Breakdown maintenance
- Corrective maintenance
fFilure Mode Effects And Criticality Analysis Example
- Now we will see failure mode effects and criticality analysis of a pump system. You will have seen in your plant there are many types of complex and critical equipment there. Like pump-motors, pump gearbox motors, compressor gearbox motors, turbine pumps, turbine gearbox pump, turbine compressor, turbine gearbox compressor, motor Fin fan, motor gearbox Fin fan, rod mill gearbox clutch motors, boilers, reactors, heat exchangers, critical valves and others of this type of many system arrangements. So in this paragraph, we will see in discussing FMECA analysis of equipment see compressor gearbox and motors what is more critical of them. Because of arrangement, the compressor is more critical than gearbox and motor. Now we try to calculate the RPN number of that system. On the basis of the measure parts of the compressor, gearbox, and motors. Above sheet is attached for RPN number of these systems.
- Here are the compressors, which have more risk of failure because more internal parts, more sensitive parts are in it as compared to the gearbox and motor. The greater RPN number is more risk of failure. Lesser the RPN number less rick to fails. We also consider during the calculation that the RPN number for FMECA involves resources like worker, engineer, designer, operator maintenance.