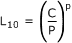What is bearing and why is it used?
A bearing is a mechanical component used to support and reduce friction between moving parts. It is a critical element in various machines and equipment that involve relative motion, such as rotating shafts or linear motion systems. Bearings enable smooth and controlled movement while minimizing wear and damage to the components involved. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery.
The primary purpose of a bearing is to facilitate the transfer of load or forces between moving parts while minimizing friction. By providing a low-friction interface between two surfaces, bearings help reduce wear and heat generation, enhancing the efficiency and longevity of mechanical systems. They are designed to carry radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft) and axial loads (parallel to the shaft) or a combination of both, depending on the specific type and configuration.
What factors are considered during selection of the machine?
- Required Functionality: The machine must meet the specific requirements and perform the desired function effectively.
- Capacity and Performance: Consider the capacity and performance specifications such as load capacity, speed, accuracy, power requirements, and cycle times.
- Size and Space Requirements: Evaluate the available space and ensure that the machine can fit within the designated area.
- Safety: Ensure that the machine has necessary safety features and meets safety standards to protect operators and comply with regulations.
- Cost and Budget: Consider the initial purchase cost, as well as long-term operating and maintenance costs, to determine the feasibility and affordability of the machine.
- Reliability and Durability: Assess the reliability and durability of the machine to ensure it can withstand the intended operating conditions and provide consistent performance over its expected lifespan.
- Compatibility and Integration: Consider compatibility with existing equipment or systems and the ease of integration into the current workflow or production line.
- Maintenance and Serviceability: Evaluate the ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and the support provided by the manufacturer or supplier.
- Operator Skill Requirements: Assess the skill level required to operate the machine and ensure it aligns with the available workforce or the ability to provide necessary training.
- Future Scalability: Consider the potential for future expansion or modifications, and whether the machine can accommodate such changes.
- Environmental Impact: Evaluate the environmental impact of the machine, such as energy consumption, emissions, waste generation, and adherence to sustainability standards.
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements: Ensure that the machine meets applicable industry standards, regulations, and certifications.
- Supplier Reputation: Consider the reputation and track record of the machine manufacturer or supplier, including customer reviews and references.
- User Feedback and Recommendations: Seek feedback from existing users or industry experts to gain insights into the machine’s performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Analyze the potential return on investment by assessing the machine’s efficiency, productivity gains, cost savings, and overall impact on the business.
These factors may vary depending on the specific industry, application, and individual requirements. It is essential to thoroughly evaluate each factor to make an informed decision when selecting a machine.
What is the function of bearing?
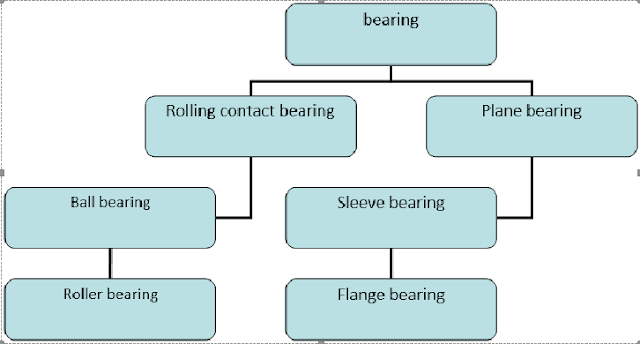
How many type of bearing?
-
Rolling element bearing
-
Ball bearing
- Deep groove ball bearing
- Angular contact ball bearing
- Self-align ball bearing
-
Roller bearing
- Taper roller bearing
- Cylindrical roller bearing
- Needle roller bearing
- Spherical roller bearing
-
-
Plane bearing
- Sleeve bearing
- Thrust bearing
- Flange bearing
- Mounted bearing
- Spherical bearing
How to calculate bearing life?
What is L 10 bearing life?
Where are bearings use?
What is the application of bearing?
Bearings have numerous applications across various industries, including:
- Automotive: Bearings are used in engines, transmissions, wheels, suspension systems, and other automotive components.
- Industrial Machinery: Bearings are essential in machines such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, turbines, and machine tools.
- Aerospace: Bearings are used in aircraft engines, landing gears, control systems, and various aircraft components.
- Power Generation: Bearings are employed in turbines, generators, wind turbines, and other power generation equipment.
- Construction and Mining: Bearings are used in heavy machinery and equipment like excavators, bulldozers, cranes, and rock crushers.
- Robotics and Automation: Bearings enable precise motion control in robotics, CNC machines, and automated manufacturing systems.
- Medical Equipment: Bearings are used in medical imaging devices, surgical equipment, dental tools, and other medical applications.
- Household Appliances: Bearings are found in appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, dishwashers, and HVAC systems.
- Marine: Bearings are used in ship propulsion systems, marine engines, and steering mechanisms.
- Agriculture: Bearings find application in agricultural machinery like tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems.
How to select bearing?
- Rpm of the equipment
- Carrying load of the machine shaft
- Difficulty of installation of bearing
- Space required for installation
- Angular and parallel misalignment tolerance
- Rigidity of the shaft and bearing both
- Torque generates during operation
- Lubrication availability
- Easy to installation and dismantle
- Thrust generate during operating
- Viscosity of the fluid
Which alloy metals used to make bearing?
Common alloy metals used to make bearings include steel, stainless steel, and bronze.
Which type of bearing is used for heavy load and high-speed application?
What is radial play in bearing?
How to select lubricant for bearing?
Selecting the appropriate lubricant for a bearing involves considering the following factors:
- Operating Conditions: Assess the speed, temperature, and load conditions in which the bearing will operate, as these factors influence the lubricant’s performance.
- Bearing Type: Different bearing types may have specific lubricant requirements, such as grease for sealed bearings or oil for open bearings.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the lubricant is compatible with the bearing material, seals, and other components to prevent any adverse reactions or damage.
- Lubrication Method: Determine whether the lubricant will be applied through oil bath, oil mist, grease, or automatic lubrication systems, and select a lubricant suitable for the chosen method.
- Viscosity: Choose a lubricant with an appropriate viscosity to provide sufficient lubrication film thickness for the bearing’s operating conditions.
- Additives: Consider the need for additives, such as anti-wear agents, corrosion inhibitors, or extreme pressure (EP) additives, based on the application requirements.
- Environmental Considerations: Assess any specific environmental factors, such as food-grade requirements, high temperatures, or exposure to water or chemicals, to select a lubricant that can withstand these conditions.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Consult the bearing manufacturer’s guidelines or recommendations for lubricant selection, as they often provide specific lubricant requirements for optimal bearing performance.
- Reliability and Maintenance: Consider the lubricant’s expected service life and the ease of maintenance, including reapplication or re-lubrication intervals.
It is crucial to consult lubricant manufacturers, bearing suppliers, or industry experts for specific guidance on selecting the most suitable lubricant for your application.
What type of bearing use in overhang centrifugal pump?
What are the types of bearings?
Some common types of bearings include ball bearings, roller bearings, thrust bearings, and plain bearings (bushings).
What factors should be considered when selecting a bearing?
Factors to consider include load capacity, speed requirements, space limitations, operating conditions, compatibility with the application, and cost.
How do bearings reduce friction?
Bearings reduce friction by providing a rolling or sliding interface between moving parts, minimizing direct contact and allowing smoother motion.
What is the difference between radial and axial loads?
Radial loads act perpendicular to the shaft’s axis, while axial loads act parallel to the shaft’s axis.
How is bearing life calculated?
Bearing life is typically calculated using the L10 life formula, which predicts the number of revolutions or hours a bearing can operate before a specific percentage (usually 10%) of a large group of bearings is expected to fail.
What is lubrication’s role in bearing performance?
Lubrication minimizes friction, reduces wear, dissipates heat, and protects against corrosion, ensuring optimal performance and extending the bearing’s lifespan.
What are the advantages of sealed bearings?
Sealed bearings provide protection against contaminants, require less maintenance, and offer improved reliability by preventing the ingress of dirt, dust, and moisture.
How does misalignment affect bearing performance?
Misalignment can lead to increased friction, premature wear, and reduced bearing life due to uneven distribution of loads and increased stress on the bearing components.
What is the difference between grease and oil lubrication?
Grease lubrication involves thicker lubricant consistency and is suitable for applications where frequent relubrication is not possible. Oil lubrication offers lower friction and dissipates heat more effectively but requires a continuous supply of lubricant.
What are the common causes of bearing failure?
Common causes include improper lubrication, contamination, excessive loads, misalignment, inadequate maintenance, and improper installation.
How can bearing noise be identified and resolved?
Bearing noise can indicate issues such as damage, misalignment, or insufficient lubrication. Identifying the root cause and resolving it may involve lubrication adjustment, bearing replacement, or addressing the underlying mechanical issues.
How can bearing life be maximized?
Maximizing bearing life involves proper lubrication, correct installation, regular maintenance, avoiding excessive loads or misalignment, and selecting the appropriate bearing for the application.
What is bearing clearance?
Bearing clearance refers to the internal space between the rolling elements and the inner and outer rings, allowing for slight movement and accommodating thermal expansion.
What is the difference between open and sealed bearings?
Open bearings have no protective seals, making them more suitable for applications with controlled environments. Sealed bearings have protective seals to prevent contamination and require less maintenance.
How can bearing preload be adjusted?
Bearing preload, which eliminates excessive internal clearance, can be adjusted by applying a specified axial force during installation or using specialized preloading methods.
How are ceramic bearings different from steel bearings?
Ceramic bearings offer higher stiffness, lower friction, and increased resistance to temperature and corrosion compared to traditional steel bearings. They are often used in high-speed and high-temperature applications.
What are the key maintenance practices for bearings?
Key maintenance practices include proper lubrication, regular inspection for signs of wear or damage, monitoring temperature and vibration, and addressing any issues promptly.
What are hybrid bearings?
Hybrid bearings combine ceramic balls with steel inner and outer rings, providing a balance between the benefits of ceramic and steel bearings, such as reduced friction and enhanced durability.