Introduction for Selecting the Right Pump for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate pump for your application is a critical part for ensuring efficiency, reliability, and longevity. This article help you through the entire process, from pump basics like process data sheet or basic date required for selection, how you can find that data as per your specific requirement. In this article you will get a selection spread sheet for choose the pump easily in less time without calculation error. So lets start our guide.
Pump Fundamentals: What You Need to Know
Either you are bigner or experienced it is crucial to understood about the function of pump of each types. In this article you will be able to understood about the pump selection.
Understanding Pump Types
Actual mainly two type of pump available in the market these are as below.
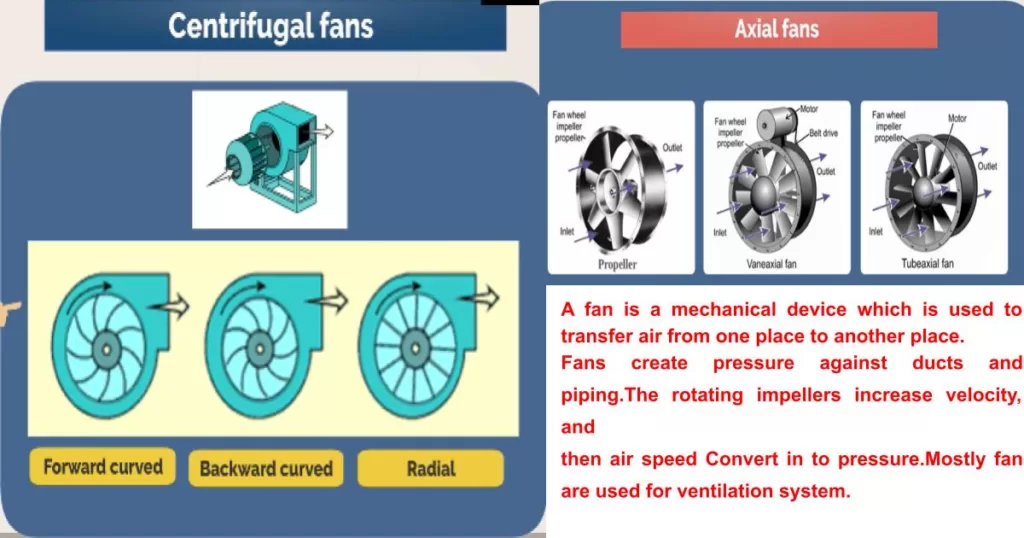
Centrifugal Pumps Fundamentals or Dynamic Pump
This is one of most common types use in the industries, due to its simplicity and high efficiency in pumping fluids. The working principle of this types of pump is simple, it convert rotational kinetic energy to hydrodynamic energy of fluid flow. generally this is best choice for less viscus fluids, and use in the water supply, sewage, and irrigation systems.
Positive Displacement Pumps Fundamentals
This is also the second most used pump in the industries and commercial application, and use for high viscus fluid with high pressure requirement, a constant flow rate, regardless of pressure variations.
This is work by take a fixed amount of services fluids and push it towards the discharge pipe, this is good for high viscus fluids like slurry and hydraulic services.
Key Factors in Pump Selection
Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements Find out required flow rate and the pressure head for your application.The pressure and pressure selection base on the where or at which height you have to pumped the liquid at the flow rate base on your application as per your operation requirements.
Generally a thumb rule is use for selection the pressure vs head, that is if you have to pump a services fluid at the height of 10 meter the pressure will of that pump minimum of 1 kg/cm2. This is use for general understanding purpose only.
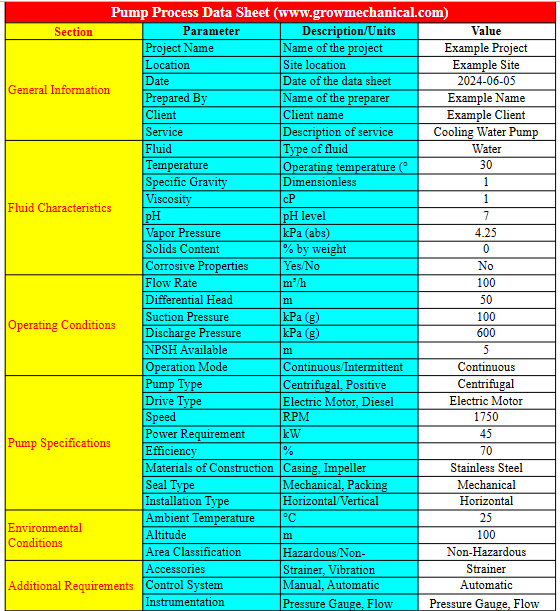
Fluid Characteristics
Consideration of the viscosity, temperature, and chemical properties of the fluid being pumped. Certain pumps handle specific fluid types better, ensuring longevity and efficiency.
- Low Viscosity (e.g., Water, Solvents) – Pump Type: Centrifugal pumps, diaphragm pumps.
- Medium Viscosity (e.g., Oils, Syrups) – Gear pumps, peristaltic pumps.
- High Viscosity (e.g., Molasses, Asphalt)- Progressive cavity pumps, screw pumps.
Fluid Density
- Low Density (e.g., Gases) – Pump Type: Vacuum pumps, blower pumps.
- High Density (e.g., Slurries, Suspensions) – Slurry pumps, diaphragm pumps.
Fluid Temperature
- Low Temperature (e.g., Refrigerants) – Cryogenic pumps.
- High Temperature (e.g., Hot Oils, Steam) – Hot oil pumps, boiler feed pumps.
Corrosive Fluids
- Corrosive (e.g., Acids, Alkalis) – Chemical pumps (made of resistant materials like stainless steel, Teflon).
- Non-Corrosive – Standard materials, depending on other fluid characteristics.
Abrasive Fluids
- Abrasive (e.g., Slurries with solid particles) – Slurry pumps, diaphragm pumps with wear-resistant parts.
- Non-Abrasive – Can use standard pumps depending on other factors.
Toxic or Hazardous Fluids
- Toxic or Hazardous (e.g., Chemicals, Solvents) – Magnetic drive pumps, hermetically sealed pumps.
Installation Environment
Check and review the physical space available for pump installation in your plants. Some pumps require more space for installation, maintenance and operation like positive displacement pump required more space than centrifugal pump.
Energy Efficiency
Choose a pump with a high energy efficiency rating to save on operational costs and reduce environmental impact.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper Alignment Ensure the pump is correctly aligned with the motor to avoid excessive wear and tear.
Regular Maintenance Perform routine checks for leaks, unusual noises, and vibrations. Regular maintenance can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the pump’s lifespan.
Monitoring System Implement a monitoring system to keep track of the pump’s performance, alerting you to any potential issues before they become major problems.
Types of Pumps and Their Applications
- Centrifugal Pumps
- Positive Displacement Pumps
- Submersible Pumps
- Peristaltic Pumps
- Diaphragm Pumps
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Pump
-
- Flow Rate
- Head (Pressure)
- Fluid Characteristics (viscosity, temperature, corrosives)
- Efficiency
- Maintenance and Reliability
Understanding Pump Curves
Explain what pump curves are and how to interpret them. Use examples and diagrams to make this section clear and practical.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting a Pump
Highlight common pitfalls and mistakes made during pump selection and how to avoid them.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Provide practical tips for maintaining pumps and troubleshooting common issues. This will help your readers ensure long-term performance and reliability.